Authors (11): L. Calvillo, F. Carraro, O. Vozniuk, V. Celorrio, L. Nodari, A. E. Russell, D. Debellis, D. J. Fermín, F. Cavani, S. Agnoli, G. Granozzi
Themes: Design DOI: 10.1039/c7ta10892c
Citations: 58
Pub type: article-journal
Pub year: 2018
Publisher: Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC)
Issue: 16
License: http://rsc.li/journals-terms-of-use
Publication date(s): 2018 (online)
Pages: 7034-7041
Volume: 6 Issue: 16
Journal: Journal of Materials Chemistry A
Link: http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlepdf/2018/TA/C7TA10892C
URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C7TA10892C
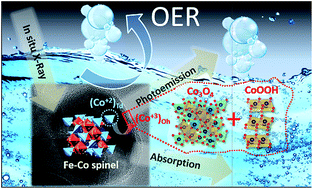
Elemental reorganisation and oxidation state changes of key active sites in Co–Fe spinels are investigated by in situ X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) and operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) under oxygen evolution operating conditions. The combination of the two techniques allows identifying both the surface and bulk modifications on the oxides and relating them to the activity loss during extended cycling. The results show that Co–Fe spinels experience a surface irreversible phase evolution under oxygen evolution reaction (OER) conditions, resulting in the formation of an amorphous layer composed of new stable Co(III) and Fe(III) species. Accelerated ageing tests show that the durability, intended as the performance loss during cycling treatments, is not directly related to the structural/chemical stability of the spinels but to the new species formed at the surface due to the electrochemical work. Thus, the material that experienced more significant changes was also the most durable one, demonstrating that the understanding of the chemical and/or structural evolution of the materials during the catalytic process can be the key for the design of highly active and stable catalysts.
| Name | Description | Publised |
|---|---|---|
| c7ta10892c1.pdf | Supl. data for Insights into the durability of Co–Fe spinel oxygen evolu... | 2018 |
<< Previous Back Next >>